An excellent presentation by former ERAU student Zack Chamberlin on asteroid mining
(download below)
Microsoft Power Point presentation [28.9 MB]
Space Terms
Allocation: Entry in the Table of Frequency Allocations of a given frequency band for the purpose of its use by one or more terrestrial or space radiocommunication services or the radio astronomy service under specified conditions. (Radio regulations)
Allotment: Entry of a designated frequency channel in an agreed plan, adopted by a competent conference, for use by one or more administrations for a terrestrial or space radiocommunication service in one or more identified countries or geographical areas and under specified conditions. (Radio regulations)
Assignment: Authorization given by an administration for a radio station to use a radio frequency or radio frequency channnel under specified conditions. (Radio regulations)
Radio regulations: The international treaty governing the use of the radio-frequency spectrum and the geostationary-satellite and non-geostationary- satellite orbits
Altitude: height of an object above mean sea level
Attitude: orientation of spacecraft in space
CHSF: Commercial Human Spaceflight operator
Crew: Any employee or independent contractor of a licensee, transferee, or permittee, or of a contractor or subcontractor of a licensee, transferee, or permittee, who performs activities in the course of that employment or contract directly relating to the launch, reentry, or other operation of or in a launch vehicle or reentry vehicle that carries human beings. A crew consists of flight crew and any remote operator.
Flight Crew: Crew that is on board a vehicle during a launch or reentry.
Expendable launch vehicle: A launch vehicle whose propulsive stages are flown only once.
Experimental permit: An authorization by the FAA to a person to launch or reenter a reusable suborbital rocket.
Flight Safety System: A system designed to limit or restrict the hazards to public health and safety and the safety of property presented by a launch vehicle or reentry vehicle while in flight by initiating and accomplishing a controlled ending to vehicle flight. A flight safety system may be destructive resulting in intentional breakup of a vehicle or nondestructive, such as engine thrust termination enabling vehicle landing or safe abort capability.
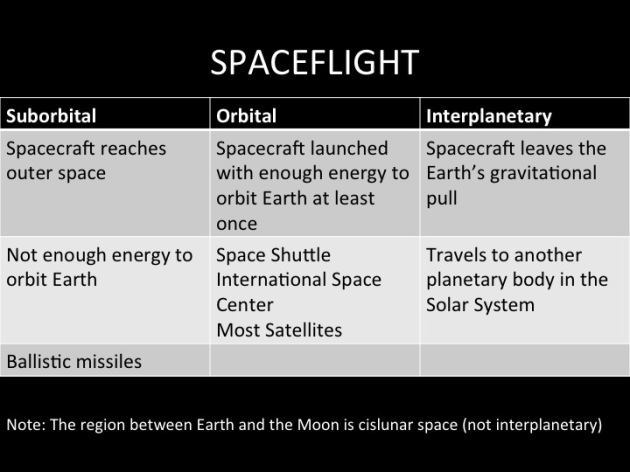
Launch: To place or try to place a launch vehicle or reentry vehicle and any payload from Earth in a suborbital trajectory, in Earth orbit in outer space, or otherwise in outer space, and includes preparing a launch vehicle for flight at a launch site in the U.S. Launch includes the flight of a launch vehicle and includes pre- and post-flight ground operations.
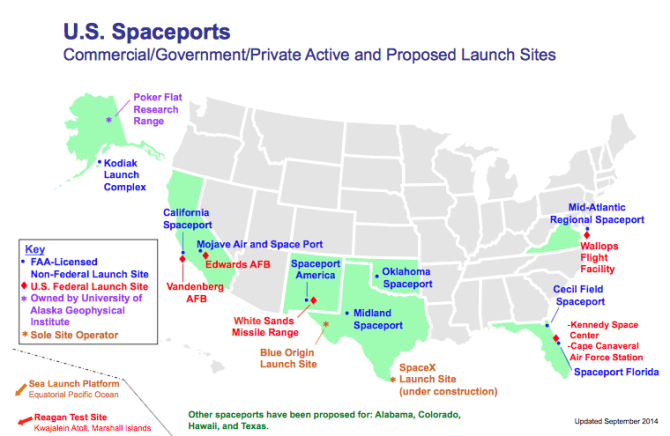
Launch site: The location on Earth from which a launch takes place (as defined in a license the Secretary issues or transfers) and necessary facilities at that location.
Launch site safety assessment (LSSA): An FAA assessment of a Federal launch range to determine if the range meets FAA safety requirements. A difference between range practice and FAA requirements is documented in the LSSA.
Launch vehicle: A vehicle built to operate in, or place a payload in, outer space or a suborbital rocket.
Inclination: angle between equatorial plane and orbit of spacecraft
Equatorial plane: imaginary line extending from the equator on Earth to the celestial sphere
Orbit: gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space
Orbital node: one of the two points where an orbit crosses a plane of reference to which it is inclined
Ascending node: point where the orbiting object moves north through the equatorial plane
Descending node: point where the orbiting object moves south through the equatorial plane
Orbital velocity: minimum speed at which a spacecraft must travel in order to remain in orbit
Period: time it takes spacecraft to make one full orbit around Earth
Apogee: point along spacecraft's orbit where it is furthest from Earth
Perigee: point along spacecraft's orbit where it is closest to Earth
Eccentricity: measure of how much an orbit deviates from a perfect circle
Karman Line: most commonly accepted earth/space boundary - at an altitude of about 100km or 62 miles
Trajectory: path that a moving object follows through space
Delta-v: measure of energy required to perform an orbital maneuver
Delta-v budget: total delta-v required to perform all of the orbital maneuvers that a spacecraft must accomplish during the course of its mission
Satellite constellation: number of satellites with coordinated ground coverage, operating together under shared control, synchronized so that they overlap well in coverage and complement with other satellites' important coverage... eg. GPS, Sirius and XM radio
Microgravity: caused by the perpetual free-fall of orbital motion; weightlessness, where the force of gravity is just above zero
Micrometeoroids: particles of dust the size of a grain of sand that date back to the creation of the solar system... eg. most shooting stars
Whipple shields: thin foils of film placed a short distance outside of the outer wall of a spacecraft to protect critical systems from macrometeoroids
Artificial Satellite: any object that has been placed into orbit by human activity
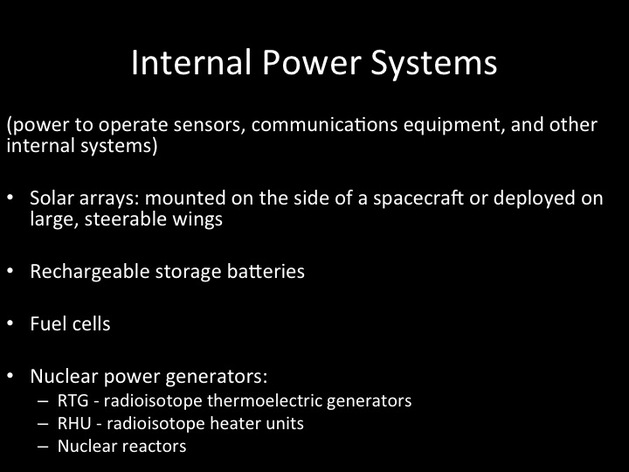
Bus: part of a satellite that carries the payload and provides electrical power, computer processors, and propulsion to the entire spacecraft
Escape velocity: velocity at which an object escapes a body's gravitational pull and will move away from that body indefinitely
Reaction mass: mass against which a system operates in order to produce acceleration
Gravity assist: field propulsion method that uses a large body's gravity like a slingshot to accelerate an interplanetary probe towards its destination
Launch window: period of time when a launch vehicle must be launched in order to reach its target in outer space
Multistage rockets: launch vehicle with multiple stages, each containing its own engines and propellant. Stages can either be parallel stages mounted alongside one another or tandem or serial stages that are mounted one on top of the other
Payload: equipment a satellite needs to perform its mission, such as cameras or transponders
Perpetual free-fall: state where an object in orbit above Earth is travelling fast enough that the curve of Earth falls away from the object at the same rate that gravity pulls the object toward Earth
Solar sail: field propulsion device that uses the pressure of solar radiation against a large collection surface to propel a spacecraft
Space adaptation syndrome: disruption of the vestibular system that causes nausea and usually affects astronauts during their first several days in outer space
Reentry site: The location n Earth where a reentry vehicle is intended to return. It includes the area within three standard deviations of the intended landing point (the predicted three-sigma footprint)
Reentry vehicle: A vehicle designed to return from Earth orbit or outer space to Earth substantially intact. A reusable launch vehicle that is designed to return from Earth orbit or outer space to Earth substantially intact is a reentry vehicle.
Reusable launch vehicle (RLV): A launch vehicle that is designed to return to Earth substantially intact and therefore may be launched more than one time or that contains vehicle stages that may be recovered by a launch operator for future use in the operation of a substantially similar launch vehicle.
Risk: A measure that accounts for both the probability of occurrence of a hazardous event and the consequence of that event to persons or property.
Space flight participant (SFP): An individual, who is not crew, carried aboard a launch vehicle or reentry vehicle.
Suborbital rocket: A vehicle, rocket-propelled in whole or in part, intended for flight on a suborbital trajectory, and the thrust of which is greater than its lift for the majority of the rocket-powered portion of its ascent.
Suborbital trajectory: The intentional fllight path of a launch vehicle, reentry vehicle, or any portion thereof, whose vacuum instantaneous impact point does not leave the surface of Earth.
Near-Earth Object (NEO): classified as meteoroids, asteroids, or comets depending on size and composition - Near-Earth Object Program
Adobe Acrobat document [79.0 KB]
WRCs: World Radiocommunication Conferences
FSS: Fixed Satellite Services
MSS: Mobile Satellite Services
BSS: Broadcasting Satellite Services
EES: Earth Exploration Services
SRS: Space Research Services
SOS: Space Operation Services
RSS: Radiodetermination Satellite Services
ISS: Inter-Satellite Services
ASS: Amateur Satellite Services
DBS: Direct Broadcast Satellite
VSAT: Very Small Aperture Terminal network
ERTS-1: Earth Resources Technology Satellite (later named Landsat-1)
MLAs: Manufacturing License Agreements
TAAs: Technical Assistance Agreements
SECs: Special Export Controls
WDA: Warehousing and Distribution Agreement
Sir Isaac Newton's laws of motion and law of universal gravitation
Laws of Motion:
- every body continues in a state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by a force imposed upon it
- when a force is applied to a body, the change of momentum is proportional to, and in the direction of, the applied force
- for every action there is an equal (in magnitude) and opposite (in direction) reaction
Law of Universal Gravitation: every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a predictable, measurable force
LEO - Low Earth Orbit (polar orbit and sun-synchronous orbit): orbit located at an altitude of between 160 and 1,000km (100-600 miles)
Polar orbit: passes above or nearly above both poles of the Earth
Sun-synchronous orbit: orbit times to pass over the same point on Earth at the same time of day
MEO - Medium Earth Orbit: orbit located at an altitude of between 1,000 and 35,786km (600-22,236 miles)
- HEO - High Earth Orbit or Highly Elliptical Orbit (Molniya Orbit): elliptical orbit that has a perigee of about 1,060km (660 miles) and an apogee of about 38,624km (24,000 miles) in a single orbital period
GEO - Geosynchronous Earth Orbit: orbit located at an altitude of exactly 35,786km (22,236 miles)
GSO - GeoStationary Orbit: geosynchronous orbit directly above the equator that appears to remain stationary over one point on Earth
GTO - Geostationary/Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (Hohmann): used to reach GEO or GSO, respectively; elliptical orbit used to move from a lower circular orbit to a higher circular orbit
Elliptical orbit
Lagrange Points: orbital locations between two large celestial bodies where the combined gravity of the objects interacts such that a smaller object placed at this point will stay in place relative to the larger bodies
Parking Orbit: temporary orbit used to store a satellite that is waiting to move on to the next stage of its mission
Graveyard Orbit: orbit several hundred miles above GSO to which GSO satellites are moved at the end of their operational life in order to make room for other satellites
ECLSS - Environmental Control and Life Support Systems
Adobe Acrobat document [1.6 MB]
Radiation Sources
(outer space is saturated with eletromagnetic radiation)
- Particles trapped in Earth's magnetic field (Van Allen radiation belts)
- particles ejected from the Sun during solar storms
- galactic cosmic rays (heavy, high-energy ions that originate outside of the solar system)
Adobe Acrobat document [12.7 MB]
Adobe Acrobat document [2.5 MB]
Adobe Acrobat document [12.2 MB]
Adobe Acrobat document [117.5 KB]
Adobe Acrobat document [156.2 KB]
Microsoft Word document [177.5 KB]
Adobe Acrobat document [792.4 KB]
Adobe Acrobat document [257.6 KB]
Adobe Acrobat document [250.3 KB]
Adobe Acrobat document [313.5 KB]
Adobe Acrobat document [326.6 KB]
Adobe Acrobat document [2.5 MB]
Contact Me
Sarah Nilsson, J.D., Ph.D., MAS
602 561 8665
You can also fill out my
Get Social with Me
Legal Disclaimer
The information on this website is for EDUCATIONAL purposes only and DOES NOT constitute legal advice.
While the author of this website is an attorney, she is not YOUR attorney, nor are you her client, until you enter into a written agreement with Nilsson Law, PLLC to provide legal services.
In no event shall Sarah Nilsson be liable for any special, indirect, or consequential damages relating to this material, for any use of this website, or for any other hyperlinked website.
Steward of
I endorse the following products
KENNON (sun shields)