Classroom Assessment: approach designed to help teacher find out what students are learning in the classroom and how well they are learning it. This approach is
- Learner-centered: focus is on observing and improving learning – often more effective to help students change their study habits or develop their metacognitive skills (skills in thinking about their own thinking and learning) – if they are to become independent, lifelong learners, students must learn to take full responsibility for their learning
- Teacher-directed: defining characteristic of any profession is that it depends on the wise and effective use of judgment and knowledge – CATs respects the autonomy, academic freedom, and professional judgment of college faculty – individual teacher decides what to assess, how to assess, and how to respond to the information gained through the assessment
- Mutually beneficial: requires active participation of students – by cooperating in assessment, student reinforce their grasp of course content and strengthen their skills at self-assessment – motivation is increased when they realize faculty are interested and invested in their success as learners – when students focus more clearly, participate more actively, and feel more confident that they can succeed, they do better in their course work
- Formative: approach to assessment – purpose is to improve the quality of student learning – CATs almost never graded and almost always anonymous – aim is to provide faculty with information on what, how much, and how well students are learning, in order to help them better prepare to succeed – on graded evaluations and in world beyond classroom
- Context-specific: have to respond to particular needs and characteristics of teachers, students, and disciplines to which they are applied – you need the right tool (CAT) to do the job right – each class has its own “chemistry” (different students and backgrounds) hence you must select the correct CAT – each class develops its own “micro culture”
- Ongoing: classroom assessment is an ongoing process – creation and maintenance of classroom “feedback loop” – CATs provide feedback from students on their learning – as this approach becomes integrated into everyday classroom activities, the communications loop connecting faculty to students – from teaching to learning – becomes more efficient and more effective
- Rooted in good teaching practice: CAT build on existing good practice by making assessment more systematic, more flexible, and more effective – taking a few minutes to administer a CAT before teaching, gives teacher a clearer idea of where the students are, and thus, where to begin instruction – during class CATs reveal how well students are following class progress – CATs after class session helps to reinforce material taught and uncovers gaps in understanding before they become impediments – directed practice in self-assessment gives students opportunity to learn metacognitive skills
7 BASIC ASSUMPTIONS OF CATs
1. The quality of student learning is directly, although not exclusively, related to the quality of teaching. Therefore, one of the most promising ways to improve learning is to improve teaching.
2. To improve their effectiveness, teachers need first to make their goals and objectives explicit and then to get specific, comprehensible feedback on the extent to which they are achieving those goals and objectives. Teaching Goals Inventory (TGI) is an instrument designed to help faculty identify and clarify their instructional goals.
CATs reinforce student learning in 3 ways:
(a) By focusing student attention on the most important elements of the course;
(b) By providing additional practice in valuable learning and thinking skills; and
(c) By training students to become more self-aware, self-assessing, independent learners.
3. To improve their learning, students need to receive appropriate and focused feedback early and often; they also need to learn how to assess their own learning.
4. The type of assessment most likely to improve teaching and learning is that conducted by faculty to answer questions they themselves have formulated in response to issues or problems in their own learning.
5. Systematic inquiry and intellectual challenge are powerful sources of motivation, growth, and renewal for college teachers, and classroom assessment can provide such challenge.
6. Classroom assessment does not require specialized training; dedicated teachers from all disciplines can carry it out.
7. By collaborating with colleagues and actively involving student in classroom assessment efforts, faculty (and students) enhance learning and personal satisfaction.
The value of starting small: a 3-step process
- Planning: select only one “focus” class to try a CAT on – a class that you are confident in and that is going well – pick one of these:
- The Minute Paper
- The Muddiest Point
- The One-Sentence Summary
- Directed Paraphrasing
- Applications Cards
- Implementing: let students know beforehand about the CAT – assure them it is to assess their learning and not grade them – best to ask for anonymous responses – ensure they understand the procedure (good idea to have it written down) – when done do a cursory read through
- Responding: close the feedback loop by letting students know what you learned from the CAT and what adjustments you intend to make based on the results – and what adjustments the students could make to improve their learning
5 SUGGESTIONS FOR A SUCCESSFUL START
- If a CAT does not appeal to your intuition and professional judgment as a teacher, do not use it
- Do not make CATs into a self-inflicted chore or burden
- Do not ask your students to use any CAT you have not previously tried on yourself
- Allow for more time than you think you will need to carry out and respond to the assessment
- Make sure to “close the loop” – let students know what you learn from their feedback and how you and they can use that information to improve learning
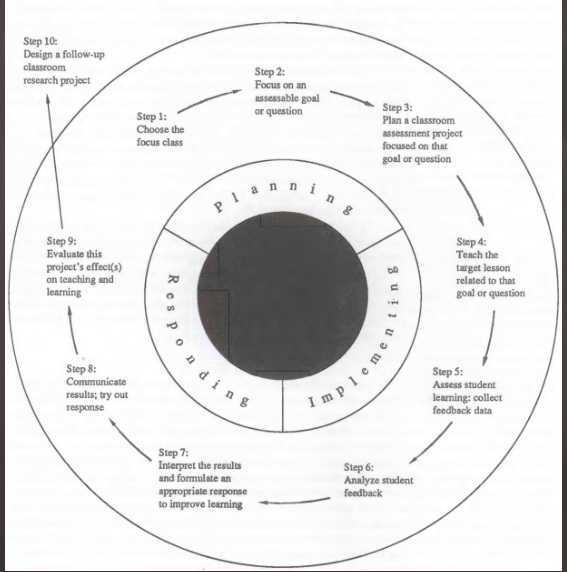
Classroom Assessment Project Cycle
Advantages of starting with goals:
- Encourages faculty to engage in a deep level of self-assessment about their teaching aims
- Enhances motivation and teacher ownership of the process by tying assessment directly to the instructional goals that individual classroom teachers value most
- Promotes good instructional practice by ensuring that faculty are assessing what they are teaching and teaching what they are assessing
- Creates the basis for a shared vocabulary, which teachers from different disciplines can use in discussing their CATs
- Offers a natural, effective way to structure future networks of participants
Disadvantages of starting with goals:
- Can initially appear somewhat complex and time-consuming
- Process of identifying and clarifying goals can seem overwhelming to some, even threatening
- Using TGI can keep the process at an abstract level longer than is comfortable for some
10 Guidelines for success and a checklist for avoiding problems:
- Start with assessable goals (right size, precisely stated, easy to assess, worth assessing, actually taught in class)
- Focus on alterable variables
- Build in success (CAT appropriate to goal, can be integrated into class activity, reasonably simple, contributes to learning)
- Start small (tried on yourself, run-through with colleague, made purpose clear to students, process clear to students, provide necessary practice, allow enough time for technique)
- Get students actively involved
- Set limits on the time and effort you will invest
- Be flexible and willing to change (analyze data, collect reasonable amount, simple analysis, enough time for analysis)
- Work with other teachers who share your interests
- Remember that students must first learn to give useful feedback – and then must practice doing so (plan the response, explicit feedback to students, presented appropriately, good and bad news, accomplish a reasonable change, allow time to respond adequately)
- Enjoy experimentation and risk-taking, not just success
ASSESSING PRIOR KNOWLEDGE, RECALL, AND UNDERSTANDING
|
Background Knowledge Probe |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
|
To assess prior learning ask students to write short answers, or circle correct responses to multiple choice or both |
|
Teachers determine starting point for lesson |
|
Students focus on subject matter, and get a preview of new stuff to come plus a review of stuff already known |
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
TGI 32 – develop an informed historical perspective |
|
Focused Listing |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
To focus students’ attention on a single important term, name, or concept from a particular lesson or class session and directs them to list several ideas that are closely related to that “focus point” |
|
Can be used before, during, and after class |
|
TGI 9 – improve skill at paying attention |
|
TGI 10 – develop ability to concentrate |
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
Misconception/Preconception Check |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
|
Assesses student prior knowledge but with a twist – focus is on uncovering prior knowledge or beliefs that may hinder or block further learning |
|
TGI 8 – develop ability to distinguish between fact and opinion |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
TGI 27 – develop an openness to new ideas |
|
TGI 50 – cultivate an active commitment to honesty |
|
Empty Outlines |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
|
Instructor provides empty or partially completed outline of in-class presentation and allows students a limited time to complete |
|
Works best in courses with large amount of content, facts, principles, in structured format |
|
TGI 9 – improve skill at paying attention |
|
TGI 10 – develop ability to concentrate |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
Memory Matrix |
||||||||||||
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - medium |
||||||||||||
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
||||||||||||
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
||||||||||||
|
2-dimensional diagram: e.g.
Rows and columns are filled in BUT cells are left empty |
||||||||||||
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
||||||||||||
|
TGI 14 – improve reading skills |
||||||||||||
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
||||||||||||
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
||||||||||||
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
Minute Paper |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Quick and extremely simple way to collect written feedback on learning |
|
Ask question: What was the most important thing you learned during this class? What important question remains unanswered? |
|
TGI 5 – develop ability to synthesize and integrate information and ideas |
|
TGI 6- develop ability to think holistically: to see the whole as well as the parts |
|
TGI 9 – improve skill at paying attention |
|
TGI 10 – develop ability to concentrate |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
Muddiest Point |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Ask question: What was the muddiest point in ___________? |
|
TGI 9 – improve skill at paying attention |
|
TGI 10 – develop ability to concentrate |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
ASSESSING SKILL IN ANALYSIS AND CRITICAL THINKING
|
Categorizing Grid |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Students are presented with a grid containing 2 or 3 important categories and a list of various items to be sorted – they are given limited time to sort into correct categories on grid |
|
TGI 2 – develop analytic skills |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observation |
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
Defining Features Matrix |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Requires students to categorize concepts according to the presence (+) or absences (-) of important defining features, thereby providing data on their analytic reading and thinking skills |
|
TGI 2 – develop analytic skills |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observation |
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 14 – improve reading skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
Pro and Con Grid |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low to medium |
|
Students make lists of pros and cons to help them think more clearly about a pressing decision |
|
TGI 2 – develop analytic skills |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observation |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 28 – develop an informed concern about contemporary social issues |
|
TGI 35 – develop capacity to make informed ethical choices |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
|
TGI 52 – develop capacity to make wise decisions |
|
Content, Form, and Function Outlines |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
This is also known as “What, how, and why Outlines” |
|
To respond to it, the student carefully analyzes the WHAT (content) HOW (form) and WHY (function) of a particular message |
|
TGI 2 – develop analytic skills |
|
TGI 14 – improve reading skills |
|
TGI 15 – improve writing skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 35 – develop capacity to make informed ethical choices |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
|
Analytic Memos |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – high |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
Basically a simulation exercise |
|
Requires students to write a 1-page or 2-page analysis of a specific problem or issue – the person for whom the memo is being written is usually identified as an employer, a client, or a stakeholder who needs the student’s analysis to inform decision making |
|
TGI 2 – develop analytic skills |
|
TGI 3 – develop problem-solving skills |
|
TGI 15 – improve writing skills |
|
TGI 37 – develop management skills |
|
TGI 38 – develop leadership skills |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
ASSESSING SKILL IN SYNTHESIS AND CREATIVE THINKING
|
One-Sentence Summary |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
|
Challenges students to answer the questions “who does what to whom, when, where, how and why?” about a given topic, and then to synthesize those answers into a single informative, grammatical, and long summary sentence |
|
TGI 5 – develop ability to synthesize and integrate information and ideas |
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 14 – improve reading skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 37 – develop management skills |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
Word Journal |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low to medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium to high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium to high |
|
Prompts a two-part response – first, student summarizes a short text in a single word – second, student writes a paragraph or two explaining why he or she chose that particular word to summarize the text – the completed response to the Word Journal is an abstract or a synopsis of the focus text |
|
TGI 5 – develop ability to synthesize and integrate information and ideas |
|
TGI 6 – develop ability to think holistically – to see the whole as well as the parts |
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 14 – improve reading skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
|
Approximate Analogies |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
|
Students simply complete the second half of an analogy – A is to B as X is to Y – for which their instructor has supplied the first half (A is to B) – since the students don’t have to use math we call them approximate |
|
TGI 5 – develop ability to synthesize and integrate information and ideas |
|
TGI 7 – develop ability to think creatively |
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
TGI 27 – develop an openness to new ideas |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
|
Concept Maps |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium to high |
|
Drawings or diagrams showing mental connections that students make between a major concept and other concepts students have learned |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observation |
|
TGI 5 – develop ability to synthesize and integrate information and ideas |
|
TGI 6 – develop ability to think holistically – to see the whole as well as the parts |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
TGI 21 – learn to understand perspectives and values of this subject |
|
TGI 27 – develop an openness to new ideas |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
|
Invented Dialogues |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium to high |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
By inventing dialogues, students synthesize their knowledge of issues, personalities, and historical periods into the form of a carefully structured, illustrative conversation |
|
There are 2 levels of “invention” – first, students carefully selecting and weaving together actual quotes from primary sources – second, they may invent reasonable quotes that fit the character of the speakers and the context |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observation |
|
TGI 5 – develop ability to synthesize and integrate information and ideas |
|
TGI 7 – develop ability to think creatively |
|
TGI 21 – learn to understand perspectives and values of this subject |
|
TGI 23 – learn techniques and methods used to gain new knowledge in this subject |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 25 – learn to appreciate important contributions to this subject |
|
TGI 32 – develop an informed historical perspective |
|
Annotated Portfolios |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
Contain a very limited number of examples of creative work, supplemented by the students’ own commentary on the significance of those examples |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 7 – develop ability to think creatively |
|
TGI 20 – develop skill in using materials, tools, and/or technology central to this subject |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 42 – develop a commitment to personal achievement |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
ASSESSING SKILL IN PROBLEM SOLVING
|
Problem Recognition Tasks |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Present students with a few examples of common problem types – students’ task is to recognize and identify the particular type of problem each example represents |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 3 – develop problem-solving skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 17 – improve mathematical skills |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 23 – learn techniques and methods used to gain new knowledge in this subject |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
What’s the Principle |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
After students figure out what type of problem they are dealing with, they often must then decide what principle or principles to apply in order to solve the problem – this CAT focuses on the second step in problem solving – it provides students with a few problems and asks them to state the principle that best applies to each problem |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 3 – develop problem-solving skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 17 – improve mathematical skills |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 23 – learn techniques and methods used to gain new knowledge in this subject |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 39 – develop a commitment to accurate work |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
Documented Problem Solutions |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium to high |
|
To become truly proficient problem solvers, students need to learn to do more than just get correct answers to textbook problems – they need to become aware of how they solved those problems and how they can adapt their problem-solving routines to deal with messy, real-world problems – this CAT prompts students to keep track of the steps they take in solving a problem – “show and tell” how they worked it out |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 3 – develop problem-solving skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 17 – improve mathematical skills |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 23 – learn techniques and methods used to gain new knowledge in this subject |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 39 – develop a commitment to accurate work |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
Audio and Videotaped Protocols |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – high |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
By studying an audio or video recording of a student talking and working through the process of solving a problem, teachers and students can get very close to an “inside view” of the problem-solving process |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 3 – develop problem-solving skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 17 – improve mathematical skills |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 23 – learn techniques and methods used to gain new knowledge in this subject |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 39 – develop a commitment to accurate work |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
ASSESSING SKILL IN APPLICATION AND PERFORMANCE
|
Directed Paraphrasing |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
|
Success depends on one’s ability to translate highly specialized information into language that clients or customers will understand |
|
Designed to assess and help develop that valuable skill – students are directed to paraphrase part of a lesson for a specific audience and purpose, using their own words |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 15 – improve writing skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
TGI 37 – develop management skills |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
Applications Cards |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low to medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low to medium |
|
After students have heard or read about an important principle, generalization, theory, or procedure, the instructor hands out an index card and asks them to write down at least one possible, real-world application for what they just learned |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observation |
|
TGI 7 – develop ability to think creatively |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
TGI 26 – develop an appreciation of the liberal arts and sciences |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
|
Student-Generated Test Questions |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium to high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium to high |
|
One of the best ways to find out how well the students understand the material is to prepare test questions and model answers |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 18 – learn terms and facts of this subject |
|
TGI 19 – learn concepts and theories in this subject |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 39 – develop a commitment to accurate work |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
Human Tableau or Class Modeling |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium to high |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
|
|
TGI 7 – develop ability to think creatively |
|
TGI 31 – develop aesthetic appreciations |
|
TGI 32 – develop an informed historical perspective |
|
TGI 36 – develop ability to wok productively with others |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
Paper or Project Prospectus |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
A prospectus is a brief, structured first draft plan for a term paper or term project |
|
Paper prospectus: prompts students to think through elements of the assignment, such as the topic, purpose, intended audience, major questions to be answered, basic organization, and time and resources required |
|
Project prospectus: may focus on tasks to be accomplished, skills to be improved, and products to be developed |
|
TGI 1 – develop ability to apply principles and generalizations already learned to new problems and situations |
|
TGI 5 – develop ability to synthesize and integrate information and ideas |
|
TGI 15 – improve writing skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 37 – develop management skills |
Microsoft Word document [62.4 KB]
Microsoft Word document [65.4 KB]
ASSESSING STUDENTS’ AWARENESS OF THEIR ATTITUDES AND VALUES
|
Classroom Opinion Polls |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low to medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Many faculty already use de facto opinion polling in their classes when they ask students to raise their hands to indicate agreement or disagreement with a particular statement |
|
This technique builds on that kind of informal polling, providing more anonymity for students and more honest and accurate data for faculty |
|
TGI 21 – learn to understand perspectives and values of this subject |
|
TGI 27 – develop an openness to new ideas |
|
TGI 28 – develop an informed concern about contemporary social issues |
|
TGI 35 – develop capacity to make informed ethical choices |
|
TGI 38 – develop leadership skills |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 47 – develop respect for others |
|
TGI 52 – develop capacity to make wise decisions |
|
Double-Entry Journals |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
Students begin by noting the ideas, assertions, and arguments in their assigned course readings that they find most meaningful and/or controversial |
|
These notes on the text are the first half of the double-entry journal |
|
The second entry explains the personal significance of the passage selected and responds to that passage – this way students engage in a dialogue with the text, exploring their reactions to the reading |
|
TGI 14 – improve reading skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 21 – learn to understand perspectives and values of this subject |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 26 – develop an appreciation of the liberal arts and sciences |
|
TGI 27 – develop an openness to new ideas |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 47 – develop respect for others |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
|
Profiles of Admirable Individuals |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
Students write a brief, focused profile of an individual – in a field related to the course – whose values, skills, or actions they greatly admire |
|
TGI 21 – learn to understand perspectives and values of this subject |
|
TGI 25 – learn to appreciate important contributions to this subject |
|
TGI 32 – develop an informed historical perspective |
|
TGI 35 – develop capacity to make informed ethical choices |
|
TGI 38 – develop leadership skills |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 47 – develop respect for others |
|
TGI 52 – develop capacity to make wise decisions |
|
Everyday Ethical Dilemmas |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
Students are presented with an abbreviated case study that poses an ethical problem related to the discipline |
|
Students respond briefly and anonymously and faculty analyze the responses in order to understand the students’ values |
|
TGI 21 – learn to understand perspectives and values of this subject |
|
TGI 25 – learn to appreciate important contributions to this subject |
|
TGI 32 – develop an informed historical perspective |
|
TGI 35 – develop capacity to make informed ethical choices |
|
TGI 38 – develop leadership skills |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 47 – develop respect for others |
|
TGI 52 – develop capacity to make wise decisions |
|
Course-Related Self-Confidence Surveys |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
The surveys consist of a few simple questions aimed at getting a rough measure of the students’ self-confidence in relation to a specific skill or ability |
|
TGI 30 – develop a lifelong love of learning |
|
TGI 37 – develop (self-) management skills |
|
TGI 38 – develop leadership skills |
|
TGI 42 – develop a commitment to personal achievement |
|
TGI 45 – improve self-esteem/self-confidence |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 48 – cultivate emotional health and well-being |
|
TGI 49 – cultivate physical health and well-being |
Microsoft Word document [106.4 KB]
ASSESSING STUDENTS’ SELF-AWARENESS AS LEARNERS
|
Focused Autobiographical Sketches |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium to high |
|
A shorter, more specific version of a personal statement or autobiographical essay |
|
Students are directed to write a one- or two-page autobiographical sketch focused on a single successful learning experience in their past – an experience relevant to learning in this particular course |
|
TGI 30 – develop a lifelong love of learning |
|
TGI 38 – develop leadership skills |
|
TGI 42 – develop a commitment to personal achievement |
|
TGI 45 – improve self-esteem/self-confidence |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 47 – develop respect for others |
|
TGI 48 – cultivate emotional health and well-being |
|
TGI 52 – develop capacity to make wise decisions |
|
Interest/Knowledge/Skills Checklists |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low to medium |
|
Brief, teacher-made versions of the commercial interest and skills inventories long used by guidance and career counselors |
|
Teachers create checklists of topics covered in their courses and skills strengthened by or required for succeeding in those courses |
|
Students rate their interest in the various topics, and assess their levels of skill or knowledge in those topics, by indicating the appropriate responses on the checklists |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 42 – develop a commitment to personal achievement |
|
TGI 44 – cultivate a sense of responsibility for one’s own behavior |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 52 – develop capacity to make wise decisions |
Microsoft Word document [114.9 KB]
Microsoft Word document [119.2 KB]
|
Goal Ranking and Matching |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low to medium |
|
Students take a few minutes to list some learning goals they hope to achieve through the course, and rank the relative importance of those goals |
|
The instructor collects student lists and matches them against course goals |
|
TGI 21 – learn to understand perspectives and values of this subject |
|
TGI 36 – develop ability to work productively with others |
|
TGI 42 – develop a commitment to personal achievement |
|
TGI 44 – cultivate a sense of responsibility for one’s own behavior |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
Self-Assessment of Ways of Learning |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium to high |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low to medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low to medium |
|
Requires faculty who use them to adopt specific theoretical frameworks for learning |
|
Prompts students to describe their general approaches to learning, or their learning styles, by comparing themselves with several different profiles and choosing those that, in their opinion, most closely resemble them |
|
TGI 21 – learn to understand perspectives and values of this subject |
|
TGI 23 – learn techniques and methods used to gain new knowledge in this subject |
|
TGI 30 – develop a lifelong love of learning |
|
TGI 37 – develop (self-) management skills |
|
TGI 42 – develop a commitment to personal achievement |
|
TGI 46 – develop a commitment to one’s own values |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
ASSESSING COURSE-RELATED LEARNING AND STUDY SKILLS, STRATEGIES, AND BEHAVIORS
|
Productive Study-Time Logs |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium to high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
Thumbnail records that students keep on how much time they spend studying for a particular class, when they study, and how productively they study at various times of the day or night |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observations |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 37 – develop (self-) management skills |
|
TGI 41 – improve ability to organize and use time effectively |
|
TGI 44 – cultivate a sense of responsibility for one’s own behavior |
|
TGI 48 – cultivate emotional health and well-being |
|
TGI 52 – develop capacity to make wise decisions |
|
Punctuated Lectures |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation - low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Requires students and teachers to go through 5 steps:
|
|
Encourages students to become self-monitoring listeners |
|
TGI 9 – improve skill at paying attention |
|
TGI 10 – develop ability to concentrate |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 44 – cultivate a sense of responsibility for one’s own behavior |
|
Process Analysis |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
Focuses students’ attention on the process – on how they do their academic work |
|
Requires that students keep records of the actual steps they take in carrying out a representative assignment and asks them to comment on the conclusions the draw about their approaches to that assignment |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 17 – improve mathematical skills |
|
TGI 20 – develop skill in using materials, tools, and/or technology central to this subject |
|
TGI 39 – develop a commitment to accurate work |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
Diagnostic Learning Logs |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – high |
|
Limited, tightly focused versions of the academic journals many teachers already use |
|
Students keep records of each class or assignment – for class sessions students write one list of main points covered that they understood and a second list of points that were unclear – for assignments students record problems encountered or errors made as well as excellent and successful responses – at regular intervals students reflect on, analyze, and summarize the information collected on their own learning – then they diagnose their strengths and weaknesses and generate possible remedies |
|
TGI 2 – develop analytic skills |
|
TGI 3 – develop problem-solving skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 22 – prepare for transfer or graduate study |
|
TGI 39 – develop a commitment to accurate work |
|
TGI 42 – develop a commitment to personal achievement |
|
TGI 43 – develop ability to perform skillfully |
|
TGI 44 – cultivate a sense of responsibility for one’s own behavior |
ASSESSING LEARNER REACTIONS TO TEACHERS AND TEACHING
|
Chain Notes |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Students pass around a large envelope on which the teacher has written one question about the class – the students had all been given index cards beforehand and have less than a minute to write a response on the index card then drop it in the envelope and pass it on |
|
TGI 9 – improve skill at paying attention |
|
TGI 10 – develop ability to concentrate |
|
TGI 12 – improve listening skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 41 – improve ability to organize and use time effectively |
|
TGI 44 – cultivate a sense of responsibility for one’s own behavior |
|
Electronic Mail Feedback |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low to medium |
|
Instructor poses a question to the class via email about his/her teaching – students respond to email with a personal message sent to mailbox |
|
TGI 20 – develop skill in using materials, tools, and/or technology central to this subject |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 36 – develop ability to work effectively with others |
|
TGI 37 – develop management skills |
|
Teacher-Designed Feedback Forms |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low to medium |
|
Short, simple, course-specific evaluation forms – from 3 – 7 questions – multiple choice or Likert scale or short fill-in answers formats |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observations |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 50 – cultivate an active commitment to honesty |
Microsoft Word document [85.5 KB]
|
Group Instructional Feedback Technique (GIFT) |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium to high |
|
Centers on getting student responses to 3 questions related to their learning:
Best if someone other than instructor administers this – determines most frequent responses – summarizes – reports back to instructor |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observations |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 36 – develop ability to work effectively with others |
|
TGI 50 – cultivate an active commitment to honesty |
|
Classroom Assessment Quality Circles |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – high |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – high |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium to high |
|
Like the Japanese management technique – quality control circles |
|
The focus is on involving groups of students in structured and ongoing assessment of course materials, activities, and assignments |
|
TGI 4 – develop ability to draw reasonable inferences from observations |
|
TGI 8 – develop ability to distinguish between fact and opinion |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 36 – develop ability to work effectively with others |
|
TGI 37 – develop management skills |
|
TGI 47 – develop respect for others |
|
TGI 50 – cultivate an active commitment to honesty |
ASSESSING LEARNER REACTIONS TO CLASS ACTIVITIES, ASSIGNMENTS, AND MATERIALS
|
RSQC2 – Recall, Summarize, Question, Comment, Connect |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low to medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
|
Teachers can use the whole thing or select individual components to administer |
|
When the whole thing is used, this 5-step protocol guides students quickly through simple recall, summary, analysis, evaluation, and synthesis exercises focusing on a previous class session |
|
TGI 5 – develop ability to synthesize and integrate information and ideas |
|
TGI 9 – improve skill at paying attention |
|
TGI 11 – improve memory skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 37 – develop (self-) management skills |
|
Group-Work Evaluations |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – medium |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Simple questionnaires used to collect feedback on students’ reactions to cooperative learning (where students work in structured groups toward an agreed-upon learning goal) and study groups |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 36 – develop ability to work effectively with others |
|
TGI 37 – develop (self-) management skills |
|
TGI 38 – develop leadership skills |
|
TGI 47 – develop respect for others |
|
TGI 50 – cultivate an active commitment to honesty |
|
Reading Rating Sheets |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low |
|
Short, simple assessment form that students fill out in response to their assigned course readings |
|
TGI 14 – improve reading skills |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 50 – cultivate an active commitment to honesty |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
Microsoft Word document [77.6 KB]
|
Assignment Assessments |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – low to medium |
|
Ask students to consider the value of the course assignments to them as learners |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 50 – cultivate an active commitment to honesty |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
|
Exam Evaluations |
|
Faculty time and energy required for preparation – low |
|
Students time and energy to respond to CAT – low to medium |
|
Faculty time and energy to analyze data – medium |
|
Students view tests and examinations as critical indicators of faculty expectations – faculty can thus use tests and exams to direct student learning |
|
Allows teachers to examine both what students think they are learning from exams and tests and students’ evaluations of the fairness, appropriateness, usefulness, and quality of tests or exams |
|
TGI 16 – develop appropriate study skills, strategies, and habits |
|
TGI 24 – learn to evaluate methods and materials in this subject |
|
TGI 50 – cultivate an active commitment to honesty |
|
TGI 51 – develop capacity to think for oneself |
Microsoft Word document [79.6 KB]
Contact Me
Sarah Nilsson, J.D., Ph.D., MAS
602 561 8665
You can also fill out my
Get Social with Me
Legal Disclaimer
The information on this website is for EDUCATIONAL purposes only and DOES NOT constitute legal advice.
While the author of this website is an attorney, she is not YOUR attorney, nor are you her client, until you enter into a written agreement with Nilsson Law, PLLC to provide legal services.
In no event shall Sarah Nilsson be liable for any special, indirect, or consequential damages relating to this material, for any use of this website, or for any other hyperlinked website.
Steward of
I endorse the following products
KENNON (sun shields)